Harrison Burnside
Riya Patel
Harrison Burnside
Riya Patel
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Introduction
There are a variety of measures that can be used to assess the development of a country or region. Some common measures of development include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita: GDP per capita is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced in a country, divided by the country's population. It is often used as a measure of a country's economic development because it reflects the average income earned by individuals in the country.
- Human Development Index (HDI): The HDI is a composite measure of a country's development that takes into account a range of factors, including life expectancy, education, and income. It is used to rank countries based on their level of development and to identify areas for improvement.
- Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): The MPI is a measure of poverty that looks at multiple dimensions of well-being, including education, health, and living standards. It is used to identify the extent of poverty in a country and to identify groups that are disproportionately affected by poverty.
- Gender Development Index (GDI): The GDI is a measure of gender-based inequalities in a country, taking into account factors such as life expectancy, education, and income. It is used to identify areas where women and girls may be disadvantaged and to track progress towards gender equality.
- Environmental Performance Index (EPI): The EPI is a measure of a country's environmental performance, taking into account factors such as air and water quality, biodiversity, and climate change. It is used to identify areas where a country may be performing poorly in terms of environmental protection and to track progress towards environmental sustainability.
Gross Domestic Product
The most basic major measure of a country’s economic development is the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP is the monetary value of ALL goods and services produced in a country in one year so it can be used to measure the TOTAL VOLUME of a country’s economy. GDP only measures DOMESTIC (NOT international impacts on the) economy using this formula: GDP = GOODS + SERVICES.
Gross National Income
Another important measure of a country’s economic and social development is the Gross National Income (GNI). GNI is the monetary value of GDP as well as the monetary value of EXPORTS minus IMPORTS in that same year which helps to account for the wealth of a nation that is lost through INTERNATIONAL trade. Many important economists will argue that GNI is a much more accurate measure of a country’s economic volume compared to GDP because of the foreign trade imbalance in almost all countries worldwide. GNI can be calculated with this formula: GNI = GDP + (EXPORTS - IMPORTS).
Per Capita Calculations
Per capita calculations are used to determine the average value of a particular statistic for a population. To calculate per capita figures, you divide the total value of a particular statistic by the population size. For example, to calculate the per capita GDP of a country, you would divide the total value of goods and services produced in the country by the country's population.
Per capita calculations are often used to make comparisons between countries or regions with different population sizes, as they allow you to adjust for differences in population size and focus on the average value of a particular statistic for a given population.
Per capita calculations can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as comparing living standards between countries, assessing the economic development of a region, or identifying trends in a particular statistic over time. However, it is important to note that per capita calculations can be influenced by a range of factors, such as the distribution of wealth and resources within a population, and should be used with caution.
Trade Deficits
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. This means that the value of the goods and services that the country imports is greater than the value of the goods and services it exports.
Trade deficits can have a variety of economic and political consequences. For example, a trade deficit may indicate that a country is relying too heavily on foreign goods and not producing enough of its own goods to meet the demand of its consumers. This can lead to a decline in domestic manufacturing and employment.
Trade deficits can also lead to an outflow of currency from a country, as the country must use its own currency to pay for the imported goods and services. This can put downward pressure on the value of the currency and make exports from the country less competitive on the global market.
Some economists argue that trade deficits are not necessarily a problem, as they can reflect a country's strengths in other areas, such as its ability to attract foreign investment or its strong services sector. However, trade deficits can also be a cause for concern if they are accompanied by other economic problems, such as high levels of debt or persistent unemployment.
Formal and Informal Economies
In Unit 2, you learned about other indicators of social levels of development: These include fertility rates, infant mortality rates, access to health care, life expectancy, and literacy rates.
Fertility rates, infant mortality rates, access to health care, life expectancy, and literacy rates are all important indicators of a population's health and well-being. These indicators can be used to measure the overall development of a country or region and to identify areas for improvement.
Fertility rates refer to the number of children that are born to a woman during her lifetime. High fertility rates can indicate a lack of access to family planning services and education, while low fertility rates can indicate a decline in population size.
Infant mortality rates refer to the number of deaths of children under the age of one per 1,000 live births. High infant mortality rates can indicate poor access to healthcare, sanitation, and nutrition, while low infant mortality rates can indicate a higher standard of living and the overall health of a population.
Access to health care is an important factor in determining the health and well-being of a population. It can include factors such as the availability of medical facilities and trained medical professionals, as well as the affordability of healthcare services.
Life expectancy is a measure of the average length of time that a person is expected to live. It is influenced by a range of factors, including access to healthcare, nutrition, and other determinants of health.
Literacy rates refer to the percentage of the population that is able to read and write. High literacy rates can indicate a high level of education and a skilled workforce, while low literacy rates can indicate a lack of access to education and a lack of opportunities for individuals to reach their full potential.
A formal economy refers to the organized, regulated, and structured economic activity that is recognized and supported by the government of a country. The informal economy refers to economic activities that are not regulated or recognized by the government. It includes activities such as informal employment, the production and sale of goods and services through informal channels, and the exchange of goods and services outside of the formal market. A country with a larger formal than the informal economy is one that is generally MORE developed for an indicator of development. A formal economy is what is included in a GDP or GNI calculation, while the informal is not!
Here are some examples of formal and informal economic activities:
Formal economy:
- Employment in a large corporation or government agency
- The sale of goods and services through a registered business
- The payment of taxes
- The use of currency as a medium of exchange
- The production of goods in a factory using modern equipment and technology
Informal economy:
- Street vending or selling goods on the black market
- Informal employment or self-employment without legal recognition or protection
- The exchange of goods and services through barter or other non-monetary forms of exchange
- The production of goods using traditional or informal methods, such as handicrafts or cottage industries
- The sale of goods and services through unregistered or informal channels
Gender Inequality and the HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite measure of human development that takes into account a range of factors, including life expectancy, education, and income. While the HDI is a useful measure of overall development, it does not take into account gender-based inequalities, which can exist even in countries with high HDI scores.
Gender inequality refers to the unequal treatment or opportunities for individuals based on their gender. This can take many forms, including discrimination in education, employment, and access to healthcare, as well as unequal power dynamics within households and communities.
Gender inequality can have serious negative impacts on the well-being and development of individuals and societies. Women and girls who face gender-based discrimination and exclusion are often denied opportunities to reach their full potential and contribute to the development of their communities and countries.
To better understand and address gender-based inequalities, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) developed the Gender Development Index (GDI), which measures gender-based inequalities in life expectancy, education, and income. The GDI is used to identify areas where women and girls may be disadvantaged and to track progress towards gender equality.
Watch the video linked here for more information about this key topic.
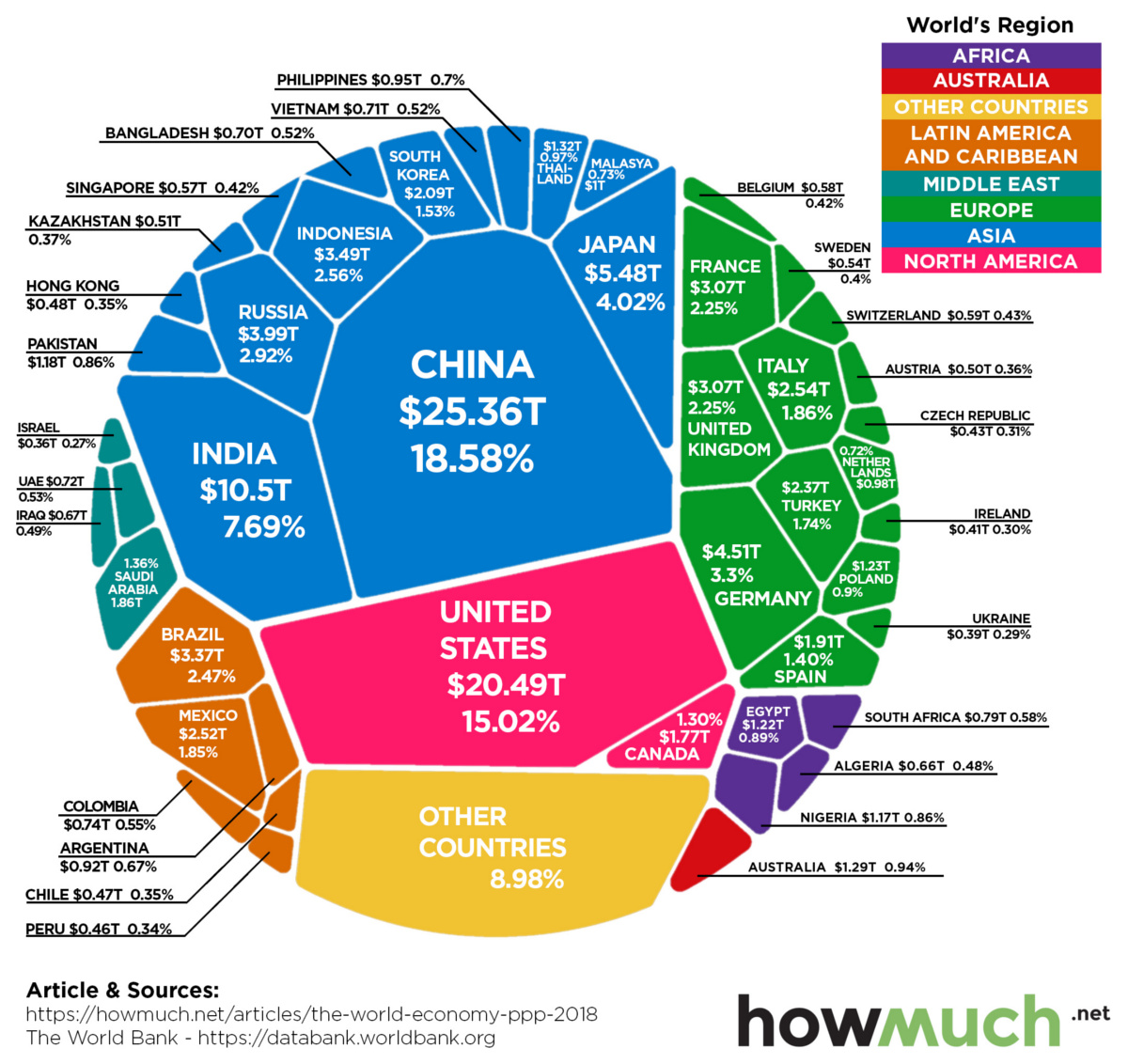
Courtesy of Howmuch
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.